Day 2 :
Keynote Forum
Bo Huang
The Chinese University of Hong Kong, Hong Kong
Keynote: Flood resilience: Measurement, validation and policy implications
Time : 10:00-10:40

Biography:
Bo Huang is a Professor in the Department of Geography and Resource Management, The Chinese University of Hong Kong, where he is also the Associate Director of Institute of Space and Earth Information Science (ISEIS). Prior to this, he held faculty positions at University of Calgary (Geomatics Engineering), Canada and National University of Singapore (Civil Engineering). He has a background and experience in diverse disciplines, including urban planning, computer science, Geographic Information Systems (GIS) and remote sensing. His research interests are broad, covering most aspects of GIScience, specifically the design and development of models in spatial/spatio-temporal statistics, remote sensing image fusion and multi-objective spatial optimization, and their applications in environmental monitoring and sustainable land use and transportation planning with consideration of resilience. He serves as the Asia-Pacific Editor of International Journal of Geographical Information Science (Taylor & Francis) and the Editor-in-Chief of Comprehensive GIS (Elsevier), a three-volume major GIS sourcebook. Currently, he is exploring along the line of geospatial big data to address sustainable spatial planning problems. He was awarded Chang Jiang Scholar Chair Professorship in 2016 by the Ministry of Education of PR China
Abstract:
Building “disaster-resilient” rather than “disaster-resistant” cities/communities requires the development of response capabilities to natural disasters and subsequent recovery. To effectively develop resilience to natural disasters, it is recognized that quantitative measurement is necessary. However, conventional indicator studies are not able to represent the multi-dimensional nature of disaster resilience, as they are unable to validate the indicator selections. In our study, a new method is devised to measure resilience using a set of indicators from the social, economic, infrastructural, and environmental domains, and which uses recovery capability to validate the indicators. Instead of using conventional data sources (e.g., census data, remote sensing data, etc.) to measure the recovery capability, a time series analysis of waste water discharge and waste gas emission data of local power plants, sewages and main factories is used to detect the changes caused by disasters, estimate the time needed for recovery, and assess recovery capability based on the calculated results. A recent record-breaking flood hazard in Changzhou in the Jiangsu province of China was selected for the case study. The proposed method for measuring recovery capability was found to complement traditional assessment methods, particularly for flood hazards. Based on the measurement outcome, ordinal logistic regression was used and infrastructural and social variables were identified as the most influential indicators for quantifying disaster resilience at the sub-district (or town) level. These findings provide insights into the multi-faceted nature of disaster resilience that will be valuable for policy-makers, and will enable them to take appropriate measures based on the identified determinants
Keynote Forum
Govind Singh Bhardwaj
Maharana Pratap University of Agriculture and Technology, India
Keynote: Landslides hazards and development of global early warning
Time : 10:40-11:20

Biography:
Govind Singh Bhardwaj is contributing the society by his nature-friendly, geo-friendly and geo-social approaches for problem solving and constructive purposes in applied and basic research in his field. His creative and innovative ideas and inputs of expertise are certainly a landmark contribution towards safe guarding the mother earth and society, using different tools available in the field of geo-science, engineering geology, and geo-technology, GIS & Remote sensing and environmental conservation. He has put forward a new concept of the geo-social development and it has been appreciated by the international gathering during the international workshop organized in the field. He has given his technical delivery with the objectivity for betterment, improvement, optimization of infrastructural developmental activities in sustainable way, by his efforts i.e. geo-electrical resistivity survey, a number of successful water supply bore wells have been located in different areas of the Rajasthan state during drought periods. He has exposure of slope stability analysis software Galena, FEA, MAT LAB, FLAGY list, FLAC 3D, GIS software TNT mips and Arc GIS, Rock ware, DIPS etc. He is working on development of earthquake and landslides early warning system for issuing global and local warnings online
Abstract:
Hilly terrain road networking throughout the world is associated with the serious problem of frequently occurring roadside landslides. The reason could be the negligence of nature friendly scientific and engineering aspects. Inconvenience consequents upon the landslides are leading to life and financial losses. Recently developed four lane road network in Aravalli is most prestigious infrastructure development activity of India. This paper is intended to explore dimensions to understand and overcome the problem of landslides. Hill slope geometry, stability analysis and finite elemental analysis help us to understand the disastrous failure of the hills, remedial measures and its suitability analysis. For development of early warning system, data were collected from hill by putting variables and constant parameters; slope stability analysis and segmentations analysis of rock mass in the hill cut face was done by using satellite data analyzed with geographic information systems software. Rock mass data, rock samples and soil samples were collected for the determination of geo-mechanical properties and slope stability analysis was carried out using licensed software GALENA. Finally computer simulation was done with the use of finite elemental analysis by generating computer models of the hill faces which are likely to fail. Complete data profile was generated and measures for controlling the landslides for selected sensitive hills
Keynote Forum
Ryuji Kohno
Yokohama National University, Japan
Keynote: Wireless Dependable IoT/M2M for Disaster Rescue and Healthcare - Reliable Machine Centric Sensing and Controlling
Time : 12:25-13:15

Biography:
Ryuji Kohno received the Ph.D. degree from the University of Tokyo in 1984. Since 1998 he has been a Professor and the Director of Centre on Medical Information and Communication Technology, in Yokohama National University in Japan. In his currier he was a director of Advanced Telecommunications Laboratory of SONY CSL during 1998-2002, directors of UWB Technology and medical ICT institutes of NICT during 2002-2012. Since 2012 he is CEO of University of Oulu Research Institute Japan – CWC-Nippon Co. Since 2007 he has been a Distinguished Professor in University of Oulu and since 2014 a director of Kanagawa Medical Device Regulatory Science Centre. He was a member of the Board of Governors of IEEE Information Theory Society in 2000-2009, and editors of IEEE Transactions on Communications, Information Theory, and ITS. He was Vice-president of Engineering Sciences Society of IEICE during 2004-2005, Editor-in chief of the IEICE Trans. Fundamentals during 2003-2005.
Abstract:
Wireless body area network (BAN) has been researched and developed for ubiquitous and remote medicine and its international standard IEEE802.15.6 was established in February, 2012. In order to find missing victims and sense their vital sign at disaster spots, highly reliable and secure, i.e. dependable BAN can be applicable to a body of robots, cars, UAVs (Unmanned Aerial Vehicle) like drones as well as a human body for dependable machine to machine (M2M) sensing and controlling. Such a M2M network can be called as "BAN of Things" like Internet of Things (IoT). Around disaster areas unexpected obstacles and complicated radio propagation tend to prevent accurate ranging and positioning, and reliable vital data sensing. To perform precise localization and robust data communications by BAN, dependable radio technologies such as ultra wide band (UWB) radio, array antenna and error-controlling codes in physical layer must be jointly optimized with MAC, Network, and application layers. Even after BAN has been developed and standardized in global, regulatory science must be keen to guarantee safety, reliability and security to be compliant for regulation. This talk will introduce research and development, standard and regulatory compliance of dependable wireless BAN for disaster rescue and medical healthcare using UWB ranging and communication. The joint Japan and New Zealand project on remote sensing and controlling multiple UAVs to locate casualties in natural disasters such as earthquakes will be also introduced. The research has two objectives, one being to use UAVs to locate people under rubble, the other to collect information that is constrained in the BANs those people are wearing. IEEE802.15 international new standard group of dependable wireless networks IEEE802.15 IG-Dependability has been chaired by the speaker.
- Coastal Geography and Floodway Analysis | Environmental Pollution | Global Warming | Meteorological Hazards
Location: Crystal
Chair
Bo Huang
The Chinese University of Hong Kong, Hong Kong
Co-Chair
Govind Singh Bhardwaj
Maharana Pratap University of Agriculture and Technology, India
Session Introduction
Mukwada G
University of the Free State, South Africa
Title: Spatiotemporal analysis of the impact of climate change on the state of vegetation cover in the Namahadi Catchment Area in South Africa.
Time : 11:35-12:00

Biography:
Mukwada G is an Associate Professor in Environmental Geography and is based at the University of the Free State in South Africa. His research primarily revolves around natural resource management, climate change and rural livelihoods. He has published more than 30 papers in accredited journals. He is the Founding Coordinator of the Afromontane Research Unit (ARU) at the University of the Free State and is the current coordinator of the Living and Doing Business in Afromontane Environments theme of the ARU.
Abstract:
Standardized Precipitation Index (SPI) values were calculated from gridded precipitation data for the Namahadi Catchment (north of the Maluti-Drakensberg Mountains) and analyzed alongside temperature data for the period between 1960 and 2015 and the SPI values were classified using the classification systems developed by McKee et al., (1993). The temperature data were analyzed for trends and spatial variability, using the Sequential Regime Shift Detection software while both temperature data and SPIs were analyzed using Geographic Information Systems, to assess temporal variations of severe and extreme drought years and their spatial magnitude. Normalized Difference Vegetation Index (NDVI) values were calculated from Landsat 8 images for randomly sampled drought years within each of the resultant epochs. The results indicate progressive warming and a temperature shift of 0.6°C between two epochs and a corresponding deterioration of vegetation cover within the catchment, indicating that climate change has affected vegetation cover negatively. This knowledge is important for the development of mitigation measures, including the restorative measures that can be considered for improving ecosystem services in the catchment.
Sofyan Sufri
Griffith University, Australia
Title: Community engagement in the early warning system (EWS) to improve disaster preparedness in Aceh province, Indonesia
Time : 12:00-12:25

Biography:
Sofyan Sufri is a PhD student at Griffith School of Medicine, Centre for Environment and Population Health, Griffith University, Queensland Australia and also serving as University Lecturer. She completed her Bachelor of Applied Science in Nursing Study Program, Health Polytechnics Ministry of Health, Banda Aceh, Indonesia. She is also a Researcher, Tsunami & Disaster Mitigation Research Center (TDMRC), Syiah Kuala University, Banda Aceh, Indonesia
Abstract:
Disasters are important global challenges due to their serious impacts on populations, economies and the environment. Global research indicates that, disasters and their associated impacts will increase due to climate change. Therefore, disaster preparedness is essential to anticipate, reduce and prepare for these disaster impacts. Within disaster preparedness, Early Warning Systems are regarded as crucial to save lives, reduce injuries, and environmental damage as they provide timely and effective information to people at risk so that appropriate responses can be taken. Many EWS heavily focus on technology and infrastructure, however disaster management research suggests that EWS need strengthened community engagement (CE) in order to enhance the effectiveness of their operation. Such research argues that ineffective responses to disaster events will continue if community engagement in EWS does not improve. Aceh, is one province in Indonesia that is vulnerable to multiple disasters. The province has achieved much progress in disaster preparedness in terms of infrastructure and capacity building for various stakeholders. However, past experience illustrates that many people engage in inappropriate actions during disaster events as they are not actively engaged with the design and operation of EWS. This has resulted in people being killed, injured or losing their property. Literature analysis points to inadequate research on enhancing community engagement especially in EWS in Aceh province. This PhD research study aims to analyse the challenges and opportunities for enhancing community engagement in Early Warning System to improve disaster preparedness in Aceh Province. The study will explore experiences, perspectives and needs of stakeholders to enhance CE in EWS in Aceh province. The research will provide strategies and recommendations for Aceh governments especially Aceh Agency for Disaster Management at provincial and District levels (BPBA and BPBD) and provide important insights into different levels of community engagement across the elements of EWS.
Nasr Bensalah
Qatar University, Qatar
Title: Addressing future challenges to reduce PFCs emissions from Aluminum smelters
Time : 14:05-14:30

Biography:
Nasr Bensalah is an Associate Professor with the Department of Chemistry and Earth Sciences, at College of Arts and Sciences, Qatar University. Since June 2009, he worked as a Research Scientist with the Department of Chemical Engineering at Texas A&M University at Qatar. Before that, he held positions of Associate Professor, Assistant Professor, and Senior Lecturer at University of Gabes in Tunisia. He is still affiliated with Gabes University as Professor of Chemistry (in leave). He has more than 15 years’ experience in teaching and research in the field of Electrochemistry. His research interests are focused on the applications of electrochemical technologies for water treatment, energy storage, and chemical analysis. He has published more than 50 papers in peer-reviewed international journals and he has supervised 8 MSc-students and 4 PhD- students. He is interested in research based on applications of electrochemical technologies for water treatment, energy storage, and chemical analysis.
Abstract:
All aluminium production has an environmental impact, such as emissions of gases (HF, SO2 and NOx) and dust into the air, in addition small amounts of greenhouse gases such as CO2 and perfluorocarbons (PFCs). In order to monitor and control the impact of these emissions, measurements and surveillance are essential. PFCs, being powerful greenhouse gases, are formed during aluminium electrolysis when so-called "anode effect" occurs. New researches have shown that PFCs may also be formed during normal electrolysis when just one or two anodes go into anode effect. The amount of PFCs formed during normal electrolysis is unknown, and therefore gas monitoring measurements on industrial cells must be performed. Low concentrations and high flow-rate volumes demand strict sampling methodologies and routines, such as EPA standards utilized world-wide. However, these standards have now come of age and new equipment has been developed and reached an affordable price level. In particular ion chromatography (IC) allows simpler handling of samples, but requires new approaches to take out the potential. The user interface of such modern devices has been standardized so that the need for specialized operators has been reduced. Additional new equipment has been introduced to measure gases in the ppb range; particularly Fourier Transform Infrared (FTIR) spectrometer. This talk focuses mainly on: (i) Representative sampling accuracy at less operating time and costs, (ii) Long-term sampling periods utilizing commercially available passive/solid absorbers, (iii) New methodologies for reducing gas emissions during aluminium production.
Amardeep Bhardwaj
Govt Of India, India
Title: Institutionalizing disaster management education and training for the World’s militaries
Time : 14:30-14:55

Biography:
Amardeep Bhardwaj is an internationally respected scholar and is a defense expert from India with 35 years of professional experience. Currently, he is holding a senior position in the Government and his prime area of focus remains Disaster Management. His academic credentials include: Master of Science, Senior Level Diploma in Management, Master of Philosophy and a PhD/Doctorate in ‘Defense Studies’ for which his thesis was titled “Role of the Armed Forces in Disaster Management”. His book captioned “Optimizing and Synergizing Disaster Response of the World’s Militaries” is nearing finalization. He has participated in actual ‘Disaster Relief Operations’ during his service. He lectures extensively on the subject, globally. Presently, he is on the Board of Management of the ‘Centre for Strategic Studies and Simulation’ at the United Services Institution of India, India’s foremost think-tank. He is also a member of ‘All India Management Association’ and ‘The International Emergency Management Society’.
Abstract:
Statement of the Problem: Viewed from a global perspective, amongst all the agencies available to mankind to combat disasters, the military has repeatedly proved itself to be the most capable. However, a few probing questions reveal the true state of affairs: how optimally are the military forces trained, equipped, organized and mandated for DM? Within the ‘training’ domain itself, are adequate number of servicemen being trained, is their education & training institutionalized, is the requisite training infrastructure in place, have training requirements been scientifically deduced, is the curriculum purposeful, is formal certification being provided, are the training institutes accredited and finally, how effective has the training proved in actual disaster operations? Truthful answers to these questions reveal the extent of the problem.
Addressing the Problem: There is a dire need to graduate from a ‘nation-specific’ to a trans-national perspective, so as to develop a globalised approach to disaster response and relief. Moreover, the military needs to get far more specialized in training and equipping itself for such complex and delicate operations. The paper outlines a bouquet of options for each military to choose from so as to optimize itself for DM.
Recommendations and Conclusion: To bring about the desired transformation the paper identifies a number of different ‘Pathways’ or ‘Approaches’. It also suggests curricula for ‘higher’ levels of education and training of the military. Further, it discusses the ‘Training Vistas’ relevant to the military and makes a strong case for it to be trained in consonance with the tasks or duties assigned to it during DRR/HADR. It concludes by showcasing a number of innovative and ‘out of the box’ solutions to significantly upgrade the military’s efficiency in executing disaster relief operations.
Constantinos S Psomopulos
University of Applied Sciences, Greece
Title: Critical energy infrastructure protection in EU legislation with a focus on natural hazards in electricity networks
Time : 14:55-15:15

Biography:
Constantinos S Psomopoulos, is a Professor and Vice President of the Electrical Engineer Dept. graduated from the School of Electrical and Computers Engineering, NTUA Greece in 1997 and received his PhD from the same School in 2002. He has worked for several years in different industrial sectors (Shipyards, Waste Management, Energy, etc). He took part as expert in energy and infrastructures, in national and international projects. He is a certified expert in Critical Energy Infrastructure Protection according to 2008/114/ EC Directive. He is the Director of the High Voltage and Power Systems Research Lab of PUAS. He joined the Academic staff of PUAS in October 2007, the research team of Earth Engineering Center of Columbia University of NY since 2011, and he is Visiting Professor in University d’ Auvergne France since June 2016. He is author of over 100 scientific papers published in international scientific journals and conferences.
Abstract:
Statement of the Problem: Since 2005, the European Program for Critical Infrastructure Protection (EPCIP) is the main policy initiative at European Union (EU) level, while Directive 2008/114/EC, "the EPCIP Directive", is the most representative legal instrument about this issue. According to the Directive 2008/114/EC, as critical infrastructure we define an asset, system or part thereof located in Member States which is essential for the maintenance of vital societal functions, health, safety, security, economic or social well-being of people, and the disruption or destruction of which would have a significant impact in a Member state as a result of the failure to maintain those functions. The energy sector is closely related with critical infrastructure protection focusing on the society protection, by protecting the energy suppliers, services and customers. This is achieved using preventive physical, cyber and operational security measures.
Methodology & Theoretical Orientation: This work presents a study about EU legislation in terms of the impact of natural hazards on the critical energy infrastructure protection considering the EU energy infrastructure program, the increasing energy demand and renewable energy sources penetration, and the experience from large scale electricity blackouts.
Findings: EC legislation provides a comprehensive view of all the problems and tasks involved at critical infrastructure protection. Despite all the efforts devoted to improving the legislation, there is a need for a more comprehensive legal framework related with the natural hazards in electricity networks.
Conclusion & Significance: Although EC legislation about critical energy infrastructure protection is steadily increased over the years, the substantial natural hazards impact in electricity systems needs to be more carefully addressed.
Kiana Kalantar
University of Tehran, Iran
Title: An individualized disaster relief solution for dust-storm situations
Time : 15:15-15:35

Biography:
Kiana Kalantar is currently majoring in Industrial Design at University of Tehran. She is the Founder and Curator of TEDxUniversityofTehran, a member of the organizing team of Startup Weekend Arts and part of executive committee at TEDxTUA. She has been a selected member of the student society at her University. And also a member of Iran’s National Elites Foundation. She is the international Gensai Design Award Winner.
Abstract:
Each year numerous cities around the world experience natural disaster permeated with fog like sand, also known as a dust storm. The dust storm was the meteorological phenomenon common in the arid and semi-arid regions. Particles will be transported by saltation and suspension, a process that moves soil from one place and deposits it in another. The Drylands around North Africa and the Arabian Peninsula are the main terrestrial sources of airborne dust. Dust storms have been shown to increase the spread of disease across the globe, like “keratoconjunctivitis” sicca ("dry eyes") or lung cancer to name a few. People in these regions are in desperate need of a clean air, a better view and a safe protection. The aim of this research is to minimize the damages caused by this kind of disasters by designing a product, that would be usable in time of need and be able to prove people living in polluted cities or stuck during a dust storm with better and safer conditions. The methodology of this research is based on data analysis, survey, observation and brain storming creative ideas focused on the most important subjects. The original goal of the project was dedicated to fix the sight problem. By creating a list of the similar devices already in the market, we set out to refine and re-design them to create a unique and original form and function. Finally, “AirBubble” is designed by author as revolutionary product that works as a multi-purpose device focused solely on preventing any damage to people’s well-beings during a dust-storm disaster. AirBubble provides all the basic needs at the time of emergency for people to be able to resume their daily life and not be stopped by the unwanted and uncharted natural disasters such as dust storms and sand storms. This product is a positive step closer to the merge of technology and designed in order to create a customized environment for an otherwise unstable geological zone.
Mahsa Ghanbari Borhan
University of Tehran, Iran
Title: How can we reduce the fatal impact of natural disasters on human life through rescue bracelet?
Time : 15:55-16:15

Biography:
Mahsa GhanbariBorhan is currently studying Industrial design in University of Tehran. She finished her 12th degree in graphic design. She teaches painting and sketching techniques. Also, she is involved in product designs for children with disabilities. Because of her graphic background, she illustrates story books for children as well. Recently, she is teaching graphic workshops in Saba art school and is consulting part-time in a research conducted in her university.
Abstract:
Every year, a large number of people around the world lose their lives because of natural disasters. Nowadays, cities have become more vulnerable, because of urbanization and population growth. Iran is considered as one of ten accident-prone countries in the world due to its geographical and geological location. So for years, the strategies such as crisis management, education, architectural design and others have been considered to reduce the impact of natural disasters on the country. Furthermore, underground constructions cause the high subside problems about 36 cm every year. This issue increases the danger of any natural damages specially earthquakes in Tehran. To decline the damages caused by natural disasters, many products have been designed but the incidents are unpredictable. In addition, we tried to design a product which is easy to use for everyday activities; not just eminently suitable for any sort of natural disaster but also useful for other highly accidental situations. According to properties of the product, after searching we found some accessories which people use every day such as: watches, bracelets, rings, etc. The aim of this research is to minimize the damages of this kind of disaster by create innovating product which can reduces the damage in dangerous conditions or incidents. This paper proposes the bracelet which is daily usable to measure and inform the person’s physical activities through intelligent electronic device during a day. The methodology of this research is based on Functional-analysis related products in these criteria. Though, we decided to design a product which can be easily carried and works with the notification systems, inform connected organizations and mobile's first aid devices about the condition of user. In fact, the bracelet works with the heart beat rate and helps to save time and accelerate assistance to find alive people.
Maryam Heydarian Ghahrodi
University of Tehran, Iran
Title: After earthquake help people by light aid; In distressed condition after earthquake search for a helpful light
Time : 15:55-16:15

Biography:
Abstract:
- Poster Presentations
Location: Foyer
Chair
Sangseom Jeong
Yonsei University, Korea
Session Introduction
Choon Yong Heng
Curtin University, Australia
Title: Doomsday rehearsal: Architecture for pre-disaster learning and 2020 Tokyo Olympics the year of disaster prevention global classroom
Time : 16:40-17:40

Biography:
Choon Yong Heng is an Architecture Enthusiast and young Architecture Graduate from the Curtin University (2017) and currently practicing at Hassell Studio, Perth. He believes that great architecture makes impactful experiences, even shapes user’s behavior on and off from the daily context. He always looks to participate in conversations on community and environmental series. His Master’s thesis expressed his concern about catastrophic contingencies reaction in the crowd. He is looking forward in more extensive research and have the intention to deliver a communication package before the year of 2020 for the Japan Department of Risk Management and Tokyo Olympics Organization Committee.
Abstract:
Statement of the Problem: Natural disaster raises awareness in contemporary capability of reacting contingencies. Japan is one most hazardous place due to its geological context. Research looked into Japanese disaster prevention culture, risk management experience and the integrity of disaster prevention facilities. Research found that Japan is successful in managing risk because of their pre-delivery of the BOUSAI disaster safety code; knowledge that reaching public consensus so that their citizens have less contradictory decisions when dealing contingencies. However, disaster prevention architecture still performs in a conventional approach. Research has aligned two strategies, BOUSAI Disaster Prevention and Tokyo Olympic Urban Development & Planning Guide. The purpose of this is to examine the feasibility of adopting education and experiential architecture in disaster prevention use.
Methodology & Theoretical Orientation: Research mapping, visual diagrams, and architectural composite drawings are utilized to conduct the design ideas. Researcher has foreseen the architectural capability to deliver great user experience in DRR strategy and utilized 2020 Olympic year as the opportunity to disseminate the BOUSAI disaster prevention ideology. Architecture is the medium to translate this prestige knowledge and introduce to the international audiences.
Outcome: The visual package has leaded the conversation of aligning Tokyo Olympic with BOUSAI to discuss over five key aspects of this alignment. It is BOUSAI re-introduction, DRR research core, immersive simulations, post-disaster living scheme, and future method of natural preservation. Researcher demonstrates BOUSAI in the transformation from written intellectual to spatial experiences. Comparative images and diagram will also be provided to show the degree of architecture contribution.
Conclusion & Significance: Disaster simulations and pre-disaster rehearse could strategically succeed in reducing disaster risk. Research expect that Tokyo Olympic is in another way to take disaster prevention education into a deeper level and globalize disaster prevention research collaboration. It also fulfills the scheme of a sustainable Post-Olympics strategy.
Dong-Hee Lim
Chungbuk National University, South Korea
Title: First principles understanding on enhanced oxidation resistance of NaBH4-treated mackinawite (FeS)
Time : 16:40-17:40

Biography:
Dong-Hee Lim received his PhD degree (2008) and worked as a Post-doc (2009-2010) in Civil and Environmental Engineering at the University of Michigan-Ann Arbor, MI, USA. He also worked as a Post-doc for two years at the Department of Energy Resources Engineering at Stanford University. He serves as an Assistant Professor in the Department of Environmental Engineering at Chungbuk National University. His research interests focus on quantum mechanics-based first principles calculations on energy and environmental-related topics. He has published 30 SCI papers.
Abstract:
Sulfide minerals are important in immobilizing toxic pollutants in reducing environments. Iron sulfide (FeS) is ubiquitous in anoxic conditions and is a good remover of various organic contaminants and heavy metals. This study was conducted to modify the FeS synthesis process to delay the air oxidation rate of FeS by adding NaBH4. Also, the fundamental mechanism of how NaBH4 enhanced the oxidation resistance of FeS was theoretically investigated by the density functional theory (DFT) calculations. The real-time oxidation test results showed that the suggested NaBH4-modification retarded the oxidation of FeS by 8 times compared to the unmodified FeS. The DFT results revealed that the FeS oxidation was attributed to sulfide oxidation of S-terminated FeS due to strong electronegativity of oxygen, and by treating FeS with the hydride ion (H−) donated from the ionization of NaBH4, less charge was withdrawn from the FeS sulfur atoms (i.e., retarded FeS oxidation) because oxidizing environment preferentially withdrew charge from the hydride ion (H−) rather than from FeS. The proposed FeS modification process may be useful in simplifying the application of reduced iron- or sulfide-minerals as alternatives to ZVI or oxide-based metal absorbents in environmental technologies. The real-time XAS measurements demonstrated that it is a useful method for accelerating kinetically slow or quasistatic equilibrium reactions. The pollutant removal efficiency of the modified FeS, compared to the unmodified FeS, will be evaluated in future studies.
Image
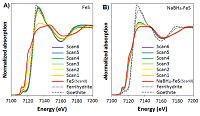
Figure 1: Fe K-edge XANES of (A) FeS and (B) NaBH4-FeS. Consecutive scans taken under atmospheric conditions were numbered from Scan 1 to 6. Scans 0 represent the XANES scans of unoxidized FeS and NaBH4-FeS. All model compounds (unoxidized FeS and NaBH4-FeS, ferrihydrite, and goethite) were scanned under a He flow, to prevent exposure to air during the measurements.
Hossein Morvaridi Farimani
University of Tehran, Iran
Title: New methodology for rescue in hazard conditions, stairway that change into slope
Time : 16:40-17:40

Biography:
Hossein Morvaridi Farimani has completed his Bachelor’s degree in Industrial Design from University of Tehran (2012-2016) and is serving as an Industrial Designer dominates on hand sketching, rendering and 3D – 2D software like Catia, SolidWorks, Rhinoceros, Sketch-up, Coreldraw, PS and etc. Also, he has achieved several courses and licenses in materials and manufacturing processes. He cooperates with several industrial companies as a Designer, like Mapna locomotive, Saipa motor company (Exterior design and prototype modeler), IranKhodro (as trainee), etc. He has experiences in management of design projects from concept creation and development through determination of manufacturing processes and final assembly details. Since November 2013, as the Head of industrial design group, he began working on the Iranian humanoid robot SURENA III, and currently he is working on the next generation of humanoid robot SURENA.
Abstract:
Since a natural disaster is most of the times unpredictable and sudden, it can cause loss of life and property damage. Here our concern is life of the populations, so the solution leads to reduce the number of victims and damages of a disaster with a simple solution. While a natural hazards or disaster happens, the moments after the occurrence time (better to call: scape time) is partly more important than the disaster itself. Former literatures has shown, 25% of the victims or injures of a natural disaster happened at the “scape time”. So with this prologue, the populations’ behaviors at scape time worth to be design. The aim of this paper is, to minimize the number of victims and damages of the disasters with a creative solution based on making daily-use products, convenient to use in hazard conditions. The methodology of this paper is based on analytical-functional procedure. Such as: survey of observation, geometric assessment of related devices and people behavior in ventures. At the moment of disaster, everyone who settle in an apartment or working in an office building try to come out of the buildings, with the elevators shutting down and with lights off, every one tend to use the stairs specially emergency stairs. Also there might be some old, injured or handicapped people in the crowd, so making the stairs convenient to use is expected. This paper proposes a design process and a new methodology, which could minimizes the damages of disasters by designing the emergency stairs or conventional stairs in a way to change into slope. The specific of this idea is to enable people to leave the buildings much faster rather than descending the stairs. The conclusions of this research were conducted to a new methodology and it consolidates the position of design in saving human’s life and decrease the number of damages. Also it’s a new idea to connect the hazard products and daily useable products and improves the efficiency and possibility of utilization of hazard products.
Han Ming Michael Koo
Curtin University, Australia
Title: The abyss: The search for a responsive underwater habitation
Time : 16:40-17:40













